The Bottom Line:
Certain red blood cell (RBC) morphologic findings may be related to an underlying disorder.
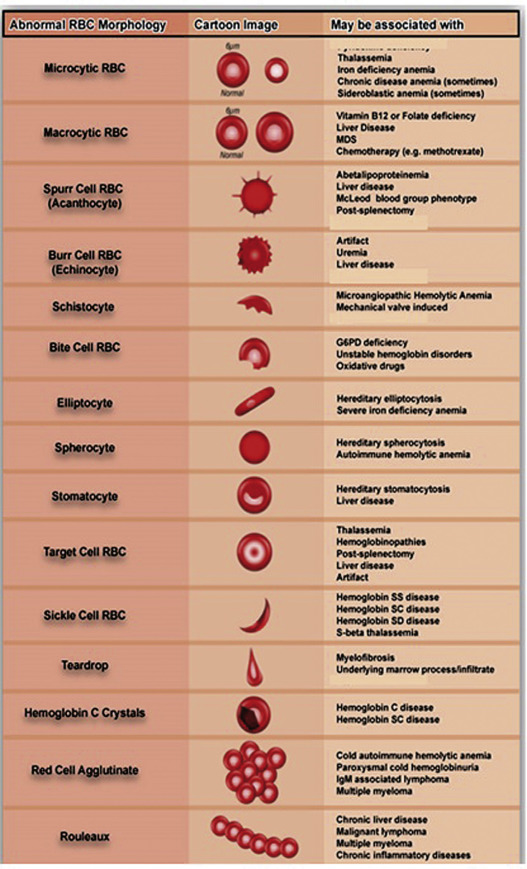
Morphologic Findings in Red Cells
| Finding | Definition | Associated Conditions | ||
| Basophilic stippling | Small blue dots in red cells, due to clusters of ribosomes | Hemolytic anemias Lead poisoning Thalassemia | ||
| Pappenheimer bodies | Larger, more irregular, and grayer than basophilic stippling, due to iron-containing mitochondria | Asplenia Sideroblastic anemia | ||
| Heinz bodies Bite cells | Heinz bodies: gray–black round inclusions, seen only with supravital stains (crystal violet). Bite cells: sharp bite-like defects in red cells where a Heinz body has been removed in the spleen. Both are due to denatured hemoglobin | Oxidative injury as found in G6PD deficiency or with unstable hemoglobins | ||
| Howell–Jolly bodies Cabot rings | Howell–Jolly body: dot-like, dark purple inclusion. Cabot ring: ring-shaped dark purple inclusion. Both represent a residual nuclear fragment | Asplenia | ||
| Target cells | Red cells with a dark circle within the central area of pallor, reflecting redundant membrane | Thalassemia Hemoglobin C Liver disease | ||
| Schistocytes | Fragmented red blood cells, with forms such as helmet-shaped cells, due to mechanical red cell fragmentation | Microangiopathic hemolytic anemias (MHA): DIC, TTP, HUS, HELLP. Mechanical heart valves | ||
| Dacrocytes (teardrop cells) | Teardrop or pear-shaped erythrocytes | Can be seen in thalassemia and megaloblastic anemia Often seen in myelophthisis | ||
| Echinocytes (burr cells) | Red blood cells that have circumferential undulations or spiny projections with pointed tips | Uremia Gastric cancer Pyruvate kinase deficiency | ||
| Acanthocytes (spur cells) | Red blood cells that have circumferential blunt and spiny projections with bulbous tips | Liver disease Abetalipoproteinemia McLeod phenotype | ||
| Spherocytes | Red cells without central pallor due to decreased red cell membrane | Immune hemolytic anemia Hereditary spherocytosis | ||
| Elliptocytes | Red cells twice as long as they are wide | Iron deficiency Hereditary elliptocytosis | ||
| Stomatocytes | Red cells whose area of central pallor is elongated in a mouth-like shape | Alcohol abuse Dilantin exposure Rh null phenotype (absence of Rh antigens) Hereditary stomatocytosis |
Rashidi HH and Green R. (2018) Red Blood Cell Morphology and Indices With Clinical Chemistry Interface. In Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, 6e. Elsevier: Philadelphia.
Mais DD. (2019). Diseases of red blood cells. In Laposata’s Laboratory Medicine: Diagnosis of Disease in the Clinical Laboratory, 3e. McGraw Hill: New York.
